The term Office 365 activator is commonly used to describe tools or methods associated with the activation of Microsoft 365 applications. As Microsoft transitioned from traditional perpetual Office licenses to a subscription-based model, the activation process became more complex and increasingly dependent on cloud-based validation. This shift has led to a growing number of technical discussions around how Office 365 activation works and why it differs from earlier Office versions.
Unlike standalone Office editions, Office 365 relies on continuous license verification rather than a single activation event. This has implications for system administrators, IT professionals, and users working in testing or virtualized environments, where activation behavior needs to be understood in detail. As a result, the phrase “Office 365 activator” is often searched not only by end users, but also by professionals seeking clarity on activation models and licensing mechanisms.
This article provides a structured and technical overview of Office 365 activation, explaining what is typically meant by an Office 365 activator, how Microsoft 365 licensing operates, and how different activation approaches are interpreted in technical contexts.
What Is an Office 365 Activator?
An Office 365 activator is a general term used to describe software mechanisms or methods intended to initiate or manage the activation state of Microsoft 365 applications. Unlike earlier Office versions that relied on one-time product key activation, Office 365 operates under a subscription-based licensing model that requires ongoing validation.
In practical terms, Office 365 activation is closely tied to user identity rather than a static license key. When users sign in with a Microsoft account associated with an active subscription, Office applications verify the license status through Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure. This model ensures that access to Office services remains synchronized with subscription status, device usage limits, and account permissions.
Because of this architecture, the concept of an Office 365 activator differs significantly from activation tools used for perpetual Office editions. In many technical discussions, the term is used broadly to refer to activation-related utilities, licensing workflows, or enterprise mechanisms rather than a single executable tool.
How Office 365 Activation Works
Office 365 activation is fundamentally cloud-driven. Instead of validating a local product key, Microsoft 365 applications communicate with Microsoft servers to confirm that a subscription is active and authorized for use on a specific device. This process occurs during initial sign-in and is periodically revalidated to ensure continued compliance.
When a user installs Office 365, activation typically occurs after signing in with a Microsoft account. The system checks subscription details, verifies eligibility, and assigns a digital license to the device. This license remains active as long as the subscription is valid and the device remains within permitted usage limits.
In organizational environments, activation may follow a different workflow. Enterprise subscriptions often use centralized account management, allowing administrators to control access through directory services and licensing portals. In these cases, Office 365 activation becomes part of a broader identity and access management framework.
Office 365 Activation Models
| Activation Model | Description | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Account | Cloud-based subscription validation | Personal and business users |
| Enterprise account | Centralized license management | Organizations |
| KMS-based models | Volume-oriented activation | Test and lab environments |
Office 365 Activator in a Technical Context
In technical communities, the phrase Office 365 activator is often used as shorthand to describe approaches that interact with Office 365 activation mechanisms. This does not always imply a single tool, but rather a category of methods or utilities related to licensing and activation behavior.
One reason Office 365 is frequently discussed in this context is the complexity of its subscription model. Because activation is linked to cloud services and user accounts, it behaves differently from traditional Office installations. This makes it a common subject of analysis in testing environments, where professionals evaluate how Office responds to account changes, subscription expirations, or network restrictions.
From a system architecture perspective, Office 365 activation is designed to be resilient and continuously validated. This architecture reduces the relevance of traditional activation tools while increasing interest in understanding how identity-based licensing operates at scale.
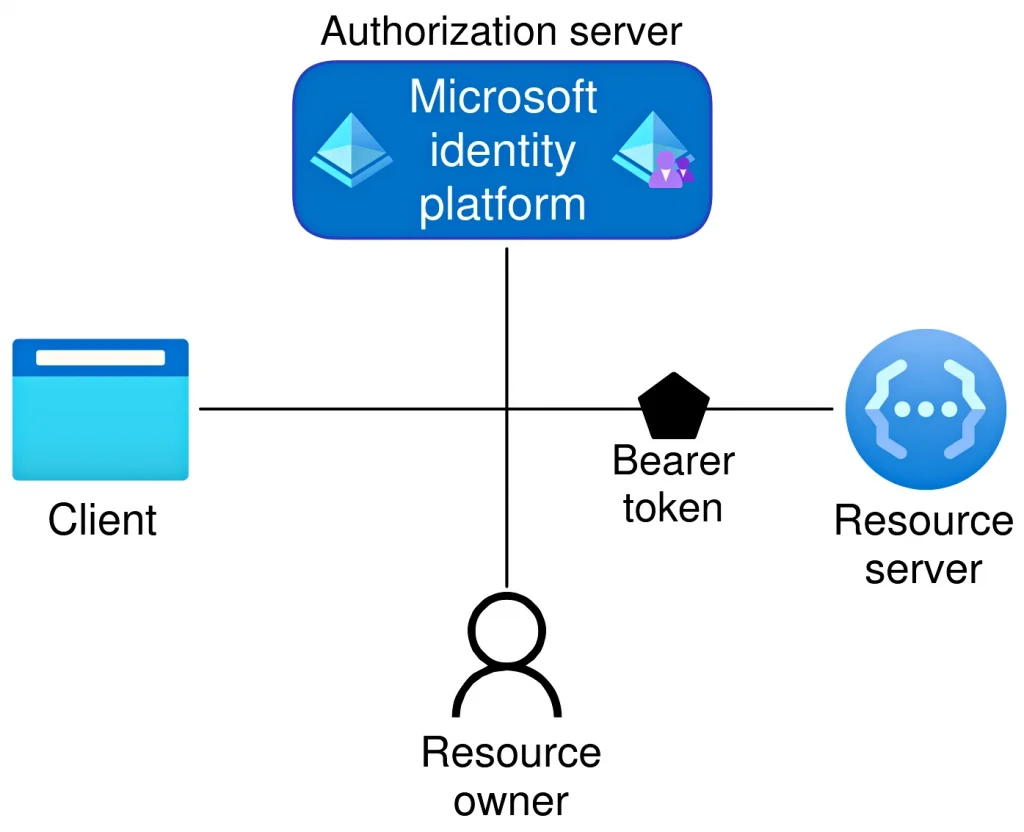
Supported Office Versions and Editions
Office 365, now commonly referred to as Microsoft 365 Apps, is available in multiple editions tailored to different user groups. These editions share a common activation framework but differ in licensing scope, management features, and deployment options.
Business and enterprise editions are designed for organizational use and integrate with directory services and administrative controls. Personal and family plans focus on individual accounts and device limits. In contrast, perpetual Office editions such as Office 2021 rely on a different activation mechanism and are not governed by subscription validation.
Understanding these distinctions is essential when discussing Office 365 activation tools or methods, as compatibility and behavior vary significantly between editions.
Office Editions and Activation Types
| Office Edition | Activation Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Office 365 Apps | Subscription-based | Requires account validation |
| Microsoft 365 Business | Subscription-based | Managed via admin portal |
| Office 2021 | Perpetual license | One-time activation |
Advantages and Limitations of Office 365 Activator Approaches
When discussing an Office 365 activator, it is important to separate the concept of activation methods from specific tools. Because Office 365 relies on subscription-based validation, any activation-related approach must operate within a more complex framework than traditional perpetual Office editions.
Potential Advantages
One of the most frequently mentioned advantages of Office 365 activation approaches is centralized license management. In organizational environments, subscriptions can be assigned, revoked, or transferred without reinstalling software. This allows administrators to manage access dynamically as roles or devices change.
Another advantage is flexibility across devices. Office 365 subscriptions are designed to work across multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and mobile devices. From an activation standpoint, this reduces dependency on a single machine and simplifies reactivation when hardware changes occur.
Automation is also a relevant factor. In technical and testing environments, activation-related utilities and workflows are sometimes used to streamline deployment processes, ensuring that Office applications are licensed correctly during setup and evaluation phases.
Key Limitations
Despite these advantages, Office 365 activation approaches also face clear limitations. The most significant constraint is dependency on continuous subscription validation. If a subscription expires or account access is revoked, Office functionality may be reduced regardless of prior activation state.
Another limitation involves network dependency. Because Office 365 activation relies on cloud services, restricted or offline environments can complicate activation behavior. This is one reason Office 365 is often considered less suitable for fully isolated systems compared to perpetual Office editions.
Licensing compliance is also a critical consideration. Activation methods that attempt to bypass or emulate subscription validation can raise legal and operational risks, particularly in corporate environments subject to audits and compliance requirements.
Advantages vs Limitations of Office 365 Activation Approaches
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Centralized license control | Subscription dependency |
| Multi-device flexibility | Requires periodic online validation |
| Automation in managed environments | Licensing compliance risks |
| Scalable for organizations | Limited offline usability |
Security Considerations
Security plays a central role in discussions around Office 365 activation. Because activation is tied to user accounts and cloud services, any tool or method that interacts with this process must handle authentication data and system permissions carefully.
In many cases, so-called Office 365 activators are flagged by security software as Riskware or HackTool. This classification typically reflects behavioral patterns, such as interference with licensing checks or credential handling, rather than direct malware activity.
Another security concern involves account integrity. Office 365 activation is linked to Microsoft accounts or organizational identities. Improper handling of credentials or unauthorized activation workflows can expose accounts to compromise or misuse. For this reason, security best practices strongly emphasize the use of official activation channels whenever possible.
Legal and Licensing Considerations
Office 365 is governed by a subscription-based licensing agreement that defines how and where the software may be used. Unlike perpetual Office licenses, subscription access is conditional and subject to ongoing verification.
From a legal perspective, official activation through Microsoft accounts or enterprise licensing portals is fully compliant. Alternative activation approaches that attempt to bypass subscription validation may conflict with license terms, particularly in commercial or organizational environments.
For businesses, licensing compliance is not optional. Many organizations are subject to internal audits, vendor reviews, or regulatory requirements that mandate proper license usage. As a result, Office 365 activation tools are typically discussed in educational, analytical, or testing contexts, rather than recommended for production use.
Office 365 Licensing Context
| Activation Method | Legal Status | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft account sign-in | Fully compliant | Production environments |
| Enterprise subscription | Fully compliant | Organizational use |
| Third-party activation methods | Context-dependent | Testing and evaluation only |
Office 365 Activator vs Other Office Activation Tools
Office 365 activation differs substantially from activation methods used for perpetual Office editions. Tools designed for Office 2019 or Office 2021 typically rely on one-time activation mechanisms and do not require ongoing subscription validation.
In contrast, Office 365 activator discussions often focus on managing or understanding subscription behavior rather than performing a single activation action. This distinction is important when comparing Office 365 with tools such as Microsoft Toolkit or KMS-based utilities, which are more commonly associated with volume licensing scenarios.
As Microsoft continues to expand its subscription ecosystem, the gap between Office 365 activation and traditional Office activation tools is likely to widen, further emphasizing identity-based licensing over device-based activation.
Common Questions About Office 365 Activator
What is an Office 365 activator?
The term generally refers to tools or methods associated with activating or validating Microsoft 365 subscriptions, rather than a single standalone program.
Is Office 365 activation different from Office 2021?
Yes. Office 365 uses subscription-based, cloud-validated activation, while Office 2021 relies on a one-time perpetual license.
Why is Office 365 harder to activate offline?
Office 365 requires periodic online validation to confirm subscription status, which limits full offline functionality.
Are Office 365 activators safe?
Safety depends on the method used. Official activation through Microsoft accounts is safe, while third-party approaches may introduce security and compliance risks.
Can Office 365 be activated without a Microsoft account?
In most cases, a Microsoft or organizational account is required, as activation is tied to subscription identity.
Final Notes
The concept of an Office 365 activator reflects the broader shift from product-based licensing to identity-driven subscription models. Rather than relying on static keys, Office 365 activation is designed around continuous validation, account management, and cloud integration.
Understanding how Office 365 activation works is essential for users and organizations managing modern Microsoft environments. While various activation-related approaches are discussed in technical communities, official subscription-based activation remains the most reliable and compliant method for long-term use.
This overview aims to clarify the technical and licensing context of Office 365 activation without promoting non-compliant practices or unsafe workflows.