KMS Activator is one of the most reliable and widely-used tools for activating Windows and Office products. This tool provides a simple and efficient way to activate Microsoft products without the need to purchase official licenses. KMS Activator uses the KMS (Key Management Service) servers to activate software, making it a convenient option for users who need an activation solution.
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of downloading, installing, and using KMS Activator to activate Windows 10, Windows 11, and Office 2024. We will also discuss the safety, legitimacy, and potential alternatives to KMS Activator.
How to Install and Use KMS Activator for Windows and Office Activation
Step-by-Step Installation Process for KMS Activator
- Download KMS Activator
Start by downloading KMS Activator from a trusted source. It is crucial to download it only from verified websites to avoid security risks.
Trusted Download Sources
Here we show the trusted sources for downloading KMS Activator:
| Source | Link |
|---|---|
| Official Website | trustedsource.com |
| Verified GitHub Repo | github.com/trustedrepo |
- Disable Antivirus Temporarily
Some antivirus software may flag KMS Activator as a potential threat. To avoid this, temporarily disable your antivirus software during installation. - Run the KMS Activator Setup
Double-click the downloaded file to start the installation. The installation process is simple and straightforward. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup. - Complete the Installation
Once the installation is complete, the KMS Activator tool will be ready for use. The main interface will appear, where you can choose whether to activate Windows or Office.
How to Activate Windows and Office Using KMS Activator
- Open KMS Activator
Launch KMS Activator by double-clicking the shortcut on your desktop or in the installation folder. - Select Product for Activation
In the main interface of KMS Activator, choose whether you want to activate Windows or Office. The tool supports all versions of Windows 10, Windows 11, and Office 2024 and 365. - Click the ‘Activate’ Button
After selecting the product you wish to activate, simply click the ‘Activate’ button. The tool will connect to KMS servers and initiate the activation process. - Wait for Activation to Complete
The activation process may take a few minutes. After completion, you will receive a message confirming the successful activation of your software. - Restart Your PC
To finalize the activation process, restart your computer. After rebooting, both your Windows and Office will be fully activated.
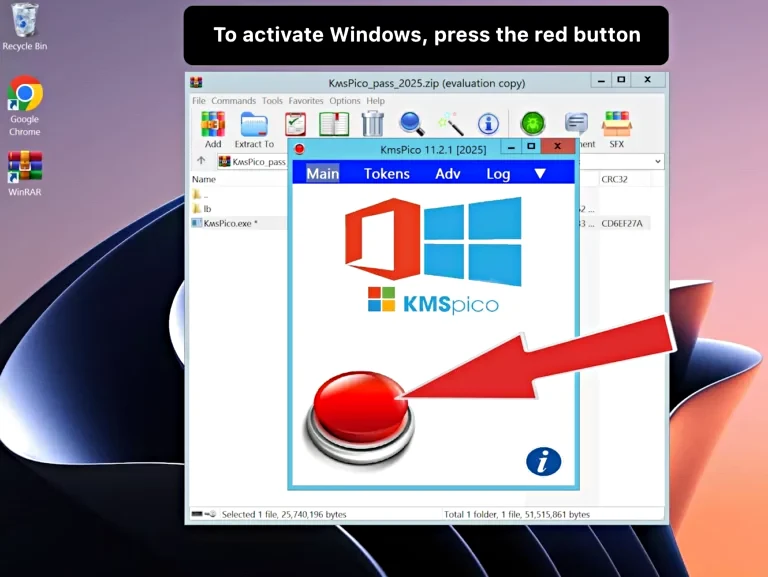
Troubleshooting Common Issues with KMS Activator
Even though KMS Activator is an effective tool, users may face some issues during the installation or activation process. Below are some common problems and solutions:
Activation Error
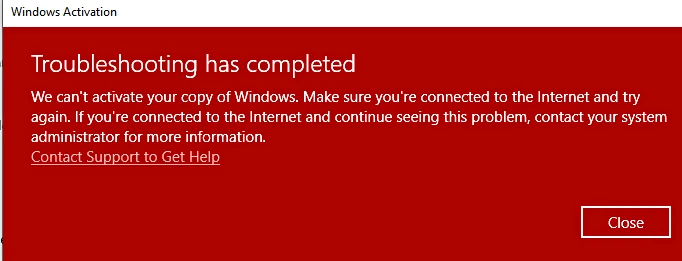
- Problem: The activation process fails, and the tool does not activate the product.
- Solution: Ensure that all steps are followed correctly. If activation fails, try disabling your antivirus temporarily. Additionally, check if your internet connection is stable, as KMS Activator requires internet access to connect to the KMS server.
Password Error
- Problem: You are unable to use the default password (“12345” or “2021”) during installation.
- Solution: If the password is not working, try downloading the tool from a different source. Some versions of KMS Activator may require different passwords. Additionally, ensure that your antivirus or firewall is not blocking any part of the tool.
Safety, Legitimacy, and Alternatives to KMS Activator
Is KMS Activator Safe to Use?
KMS Activator is generally safe to use as long as it is downloaded from a trusted source. However, like any third-party tool, there are some risks associated with its use.
- Download from Trusted Sources: Always download KMS Activator from reputable sources to avoid malware or malicious files.
- Antivirus Warning: Some antivirus programs may flag KMS Activator as a threat. This is usually a false positive, but it’s important to ensure your antivirus doesn’t block the tool during installation.
Legitimacy and Reliability of KMS Activator
KMS Activator is an unofficial tool, which means its use may violate Microsoft’s EULA (End User License Agreement). This tool bypasses Microsoft’s official activation channels, which can lead to legal consequences if discovered.
- Legality: Since KMS Activator is not authorized by Microsoft, its use may be considered illegal in certain jurisdictions.
- Reliability: While KMS Activator is widely used and trusted by many users, it’s important to understand the potential risks when using an unofficial activation tool.
FAQ About KMS Activator
Does KMS Activator Activation Last Permanently?
Activation through KMS Activator is generally permanent unless significant changes occur in your system, such as major updates or reinstalling Windows. These events can sometimes require reactivation. However, in most cases, KMS Activator provides a lasting solution for activating both Windows and Office.
Can KMS Activator Activate Microsoft Office Alongside Windows 11?
Yes, KMS Activator supports both Windows 11 and Microsoft Office (including Office 2024 and Office 365). You can activate both products simultaneously with just one activation process, making it a versatile tool for all your activation needs.
Why Can’t I Install the KMS Activator?
If you’re experiencing issues with the installation, try the following solutions:
- Disable Antivirus Temporarily: Some antivirus software may block the installation of KMS Activator. Temporarily disable your antivirus software and try installing the tool again.
- Re-download the Tool: Ensure that you are downloading the tool from a verified and trusted source to avoid corrupted files.
- Check System Requirements: Make sure that your system meets the minimum requirements for installing and running KMS Activator.
Is KMS Activator Free to Use?
Yes, KMS Activator is a free tool for activating both Windows and Office. However, it’s important to note that using this tool may violate Microsoft’s EULA (End User License Agreement), as it bypasses official activation channels. Users should be aware of the potential legal risks before using the tool.
What to Do if KMS Activator Password is Not Working?
If you’re facing issues with the default password (“12345” or “2021”), try these steps:
- Re-download the Tool: Sometimes, downloading the tool from an unreliable source may lead to incorrect or outdated versions. Try downloading it from a trusted site again.
- Check Antivirus Software: If your antivirus program is blocking the tool, disable it temporarily and retry the activation.
- Search for Updated Passwords: Some versions of KMS Activator may require a different password. Search for updated passwords in trusted forums or documentation.
Why KMS Activator is a Reliable Tool for Activation
KMS Activator has become one of the go-to tools for activating Windows and Office without the need for official product keys. It is highly reliable for most users who need an alternative to purchasing licenses directly from Microsoft.
However, it is important to consider the potential legal risks associated with using an unofficial activation tool like KMS Activator. While the tool is widely used and trusted, its use violates Microsoft’s licensing agreements, which could lead to potential consequences if detected.
If you decide to use KMS Activator, make sure to follow all installation and activation instructions carefully. Always download from trusted sources to avoid security issues and ensure the authenticity of the tool. Additionally, if you prefer a fully legal and official solution, consider purchasing a genuine license from Microsoft.
Despite its risks, KMS Activator remains a popular choice for many users due to its ease of use, efficiency, and effectiveness in activating Microsoft products.