Microsoft Toolkit is a multifunctional utility that has been widely discussed in technical communities for more than a decade. It is commonly referenced in relation to Windows and Microsoft Office activation scenarios, particularly in environments where centralized license management and automated processes are required. Over time, Microsoft Toolkit has evolved into a complex package that combines activation-related components with system diagnostics and management features.
Unlike basic single-purpose tools, Microsoft Toolkit is often described as an advanced solution designed for users who are familiar with Microsoft licensing models and enterprise software deployment concepts. This is one of the reasons it continues to attract attention from system administrators, IT specialists, and technically inclined users searching for detailed information rather than quick instructions.
This article provides a technical and analytical overview of Microsoft Toolkit, focusing on its structure, core components, supported products, and usage context. The goal is to explain how Microsoft Toolkit is positioned within activation technologies, what functions it offers, and which considerations are typically associated with its use.
What Is Microsoft Toolkit
Microsoft Toolkit is a software package designed to manage and simulate activation-related processes for certain Microsoft products, primarily Windows operating systems and Microsoft Office suites. It is commonly associated with Key Management Service (KMS)–based activation models, which are traditionally used in corporate and organizational environments.
At a high level, Microsoft Toolkit functions as an integrated environment that brings together multiple modules under a single interface. These modules are responsible for handling activation status checks, license data processing, and system-level interactions related to Microsoft software licensing. Because of this modular structure, Microsoft Toolkit is often categorized as a comprehensive activation framework rather than a simple utility.
The tool gained popularity due to its broad compatibility range and its ability to work with multiple Microsoft product generations. As Microsoft licensing systems became more complex, interest in centralized tools capable of handling various activation scenarios increased, contributing to Microsoft Toolkit’s continued visibility in search results and technical discussions.

Core Components of Microsoft Toolkit
One of the defining characteristics of Microsoft Toolkit is its modular architecture. Instead of relying on a single function, it integrates several components that address different aspects of activation and system management.
Activation Module
The activation module is the most frequently discussed component of Microsoft Toolkit. It is designed to interact with Microsoft activation mechanisms at a logical level, focusing on volume licensing concepts rather than individual retail keys. From a technical perspective, this module is structured to communicate with activation services in a way that mirrors enterprise deployment models.
Rather than offering a one-click solution, the activation module emphasizes configurability. This design reflects its original orientation toward advanced users who understand activation workflows and system requirements.
License Management Features
Another key component is license management. Microsoft Toolkit includes features that allow users to review licensing status, detect installed license types, and analyze how Microsoft products are registered within the system. These features are particularly relevant in environments where multiple Microsoft applications coexist and licensing consistency must be verified.
License management functionality also helps explain why Microsoft Toolkit is often described as more complex than entry-level activation utilities. It focuses on visibility and control rather than simplicity alone.
Diagnostic and Utility Tools
Beyond activation and licensing, Microsoft Toolkit incorporates a set of diagnostic and utility tools. These tools are intended to provide system-level insights, such as activation status reporting, service availability checks, and environment validation. In technical discussions, these utilities are often cited as the reason Microsoft Toolkit appeals to experienced users rather than beginners.
Main Modules of Microsoft Toolkit
| Module | Primary Function | Typical Context |
|---|---|---|
| Activation Module | Handles activation logic | Volume licensing scenarios |
| License Management | Reviews license status | Multi-product systems |
| Diagnostic Tools | System and service checks | Troubleshooting and testing |
Supported Microsoft Products
Compatibility is one of the main factors behind the sustained interest in Microsoft Toolkit. The tool is commonly associated with support for multiple generations of Microsoft operating systems and productivity suites, especially those distributed under volume licensing models.
Microsoft Toolkit is frequently referenced in relation to Windows desktop operating systems, as well as Microsoft Office editions designed for organizational deployment. However, compatibility often depends on specific versions, system configurations, and licensing structures rather than broad universal support.
Compatibility Overview
| Product Category | Commonly Referenced Versions | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Windows OS | Windows 7, 8, 10, 11 | Edition-dependent |
| Microsoft Office | 2013–2021 | Volume editions preferred |
| Server Products | Limited references | Context-specific |
How Microsoft Toolkit Works (High-Level Explanation)
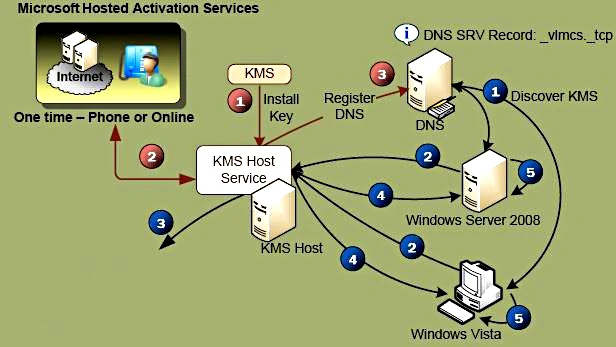
From a technical standpoint, Microsoft Toolkit is often associated with KMS-based activation concepts. KMS, or Key Management Service, is an activation technology originally designed for enterprise environments where multiple systems need to be activated without individual product keys.
Microsoft Toolkit operates by interacting with these activation principles at a system level. Instead of embedding permanent changes into individual applications, it works through service emulation and licensing state manipulation that reflects how corporate activation infrastructures function.
It is important to understand that this process is typically discussed in abstract or architectural terms. Technical explanations focus on how activation requests are handled, how licensing states are evaluated, and how enterprise activation models differ from consumer retail activation.
Microsoft Toolkit in Corporate and Testing Environments
Microsoft Toolkit is frequently mentioned in discussions related to testing environments, virtual machines, and isolated systems where activation behavior needs to be observed or validated. In such contexts, IT specialists may analyze how Microsoft products respond to different licensing configurations without deploying full production infrastructure.
In corporate settings, activation technologies are often evaluated in controlled conditions before large-scale deployment. This has led to ongoing interest in tools that replicate or simulate licensing behavior for educational, analytical, or laboratory purposes. Microsoft Toolkit is commonly referenced in these conversations due to its consolidated feature set and technical scope.
Advantages and Limitations of Microsoft Toolkit
When evaluating Microsoft Toolkit from a technical perspective, it is important to consider both its functional strengths and its structural limitations. The tool is often discussed not because it offers a perfect solution, but because it occupies a specific niche within activation-related utilities.
Potential Advantages
One of the commonly cited advantages of Microsoft Toolkit is its consolidated architecture. Instead of relying on multiple standalone utilities, users interact with a single environment that brings together activation logic, license visibility, and system diagnostics. For advanced users, this centralization reduces the need to switch between separate tools.
Another notable aspect is its broad scope. Microsoft Toolkit is frequently referenced in relation to multiple Microsoft product generations, which makes it relevant for environments where different versions of Windows and Office coexist. This is particularly useful in test labs or mixed deployments where consistency across products must be evaluated.
Flexibility is also mentioned as a distinguishing factor. Rather than enforcing a simplified workflow, Microsoft Toolkit allows users to interact with activation concepts at a deeper level. This design aligns with users who prefer transparency and control over automation.
Known Limitations
Despite its technical depth, Microsoft Toolkit is associated with several important limitations. One of the most frequently discussed concerns relates to system integrity. Because the tool interacts with licensing components and system services, it may introduce conflicts with updates, security mechanisms, or future software changes.
Another limitation involves compliance. Microsoft Toolkit operates outside official activation channels, which raises questions about licensing alignment in production environments. As a result, it is generally discussed in theoretical, testing, or educational contexts rather than as a long-term deployment solution.
Maintenance and continuity are also relevant considerations. Like many specialized utilities, Microsoft Toolkit’s development lifecycle is not tied to official product roadmaps. This can affect compatibility with newer operating system updates or changes in activation frameworks.
Advantages vs Limitations of Microsoft Toolkit
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Centralized functionality | Potential system conflicts |
| Broad product scope | Licensing compliance concerns |
| Advanced configuration options | Update compatibility risks |
| Diagnostic visibility | Limited long-term support guarantees |
Security Considerations
Security is one of the most frequently raised topics in discussions surrounding Microsoft Toolkit. From a technical security standpoint, the tool is often categorized as a “HackTool” or “Riskware” by antivirus solutions. This classification does not necessarily indicate malicious intent, but rather reflects the tool’s ability to modify system-level components.
Microsoft Toolkit interacts with licensing services, activation states, and related system processes. Any application that performs such actions is likely to trigger heuristic detection mechanisms, especially in environments with strict endpoint protection policies.
Another important factor is source integrity. As Microsoft Toolkit is not distributed through official Microsoft channels, verifying authenticity and integrity becomes a critical concern. In enterprise or sensitive environments, this alone is often sufficient reason to avoid direct use outside controlled test systems.
From a risk management perspective, Microsoft Toolkit is generally discussed as a tool that requires a clear understanding of system behavior, security implications, and potential side effects. This is one of the reasons it is more commonly referenced in technical analyses rather than general consumer guides.
Microsoft Toolkit vs Other Activation Tools
Microsoft Toolkit is frequently compared to other activation-related utilities due to its scope and complexity. While many tools focus on automation or simplicity, Microsoft Toolkit is typically positioned as an advanced, multifunctional option.
Comparison of Common Activation Tools
| Tool Name | Functional Scope | Typical User Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Toolkit | Windows & Office, advanced features | IT specialists, advanced users |
| KMSPico | Simplified activation | Entry-level users |
| KMSAuto | Automated batch processing | Bulk or repetitive scenarios |
| Manual KMS setup | Native enterprise approach | Corporate environments |
The comparison highlights that Microsoft Toolkit is not necessarily designed to replace enterprise activation infrastructure. Instead, it is often discussed as a technical reference point for understanding how different activation approaches vary in complexity and control.
Common Questions About Microsoft Toolkit
What is Microsoft Toolkit primarily used for?
Microsoft Toolkit is typically referenced as a multifunctional utility related to activation concepts, licensing visibility, and system-level diagnostics for Microsoft products.
Is Microsoft Toolkit an official Microsoft product?
No. Microsoft Toolkit is not developed or distributed by Microsoft and does not represent an official activation solution.
Why do antivirus programs detect Microsoft Toolkit?
Detection usually occurs because the tool modifies or interacts with system services and licensing components, which triggers heuristic security rules.
Does Microsoft Toolkit support newer Windows versions?
Support is often discussed in relation to specific builds and editions. Compatibility may vary depending on system updates and configuration.
Can Microsoft Toolkit be used in production environments?
It is generally discussed in testing, educational, or analytical contexts rather than as a production deployment tool.
Final Notes
Microsoft Toolkit remains a widely searched and discussed topic due to its technical scope and its association with Microsoft activation frameworks. Rather than serving as a simple solution, it represents a broader category of tools that interact with licensing systems at an architectural level.
Understanding Microsoft Toolkit requires familiarity with enterprise activation concepts, system services, and licensing models. For this reason, it continues to attract attention from technically oriented users seeking deeper insight into how Microsoft software activation functions behind the scenes.
This overview is intended to provide a structured, neutral explanation of Microsoft Toolkit, its components, and the considerations commonly associated with its use, without promoting or endorsing any specific activation method.